
Present Value of a Bond Present Value of a bond is used to determine the current market price of a bond , that may pay regular interest payments, and is redeemable at some time in the future for a specific price. Use the present value of a bond calculator below to solve the formula. Calculate the value of a bond based on the series, denomination and issue date entered.
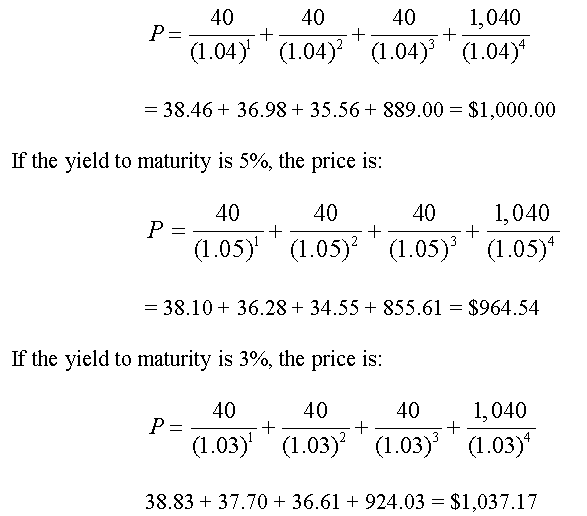
Store savings bond information you enter so you can view it again at a later date. The Savings Bond Calculator WILL NOT: Verify whether or not you own bonds. Guarantee the serial number you enter is valid. This requires us to know the interest payment amount, the current period market rate (or discount rate), and the number of periods remaining until the bond matures. This page contains a bond pricing calculator which tells you what a bond should trade at based upon the par value of the bond and current yields available in the market.
Our free online Bond Valuation Calculator makes it easy to calculate the market value of a bond. To use our free Bond Valuation Calculator just enter in the bond face value , months until the bonds maturity date, the bond coupon rate percentage , the current market rate percentage (discount rate), and then press the calculate button. How do you calculate the current yield of a bond?
How to calculate an APY of a bond? What is the current value of this bond? The present value of the bond is $ 100x 0. Add the present value of the two cash flows to determine the total present value of the bond.
Once open, choose the series and denomination of your paper bond from the series and denomination drop-down boxes. Enter the issue date that is printed on the paper bond. Present Value Calculator This present value calculator can be used to calculate the present value of a certain amount of money in the future or periodical annuity payments. The future value calculator can be used to determine future value , or FV, in financing.
FV is simply what money is expected to be worth in the future. Typically, cash in a savings account or a hold in a bond purchase earns compound interest and so has a different value in. The purpose of this calculator is to provide calculations and details for bond valuation problems. It is assumed that all bonds pay interest semi-annually.
Future versions of this calculator will allow for different interest frequency. Code to add this calci to your website Just copy and paste the below code to your webpage where you want to display this calculator. There is in depth information on this topic below the tool. Notice here that Pmt = $in the Function Arguments Box. We calculated the rate an investor would earn reinvesting every coupon payment at the current rate, then determining the present value of those cash flows.

Present value is compound interest in reverse: finding the amount you would need to invest today in order to have a specified balance in the future. See How Finance Works for the present value formula. You can also sometimes estimate present value with The Rule of 72.
Extensive effort is made to ensure the data provided is accurate. Search for Bond Calculator. Find Bond Calculator. Bond values are very sensitive to market interest rates.
Use this calculator to help determine the value of a bond. Pricing of a bond or bond valuation is the determination of the fair value or fair price of the bond , which is nothing but the sum of present values of all the coupon (interest) payments from the bond and the final redemption amount, discounted at the required rate of return (yield). We express the discount rate as a percentage, and it is used to calculate the PV. And while the calculation is exact (a change of one day changes the calculated result), the present value itself is a personal number.
We calculate these two present values by discounting the future cash amounts by the market interest rate per semiannual period. Here is an example calculation for the purchase price of a $000face value bond with a year duration and a annual interest rate. The term discount bond is used to reference how it is sold originally at a discount from its face value instead of standard pricing with periodic dividend payments as seen otherwise.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.